Where to pay less taxes on an inheritance
Catalonia, Cantabria and Madrid are the autonomous communities with the most tax advantages in matters of inheritance, while Andalusia, Asturias and Murcia are the most expensive and apply state regulations.
All Spaniards are equal before the law, but not so much before the Treasury. After the latest reforms introduced in tax matters, inequalities are growing depending on the Autonomous Community in which one lives. In addition to the exceptions that already existed in the Basque Country or Navarra, due to the regional regime, regional regulations are added that freely decide the application of some taxes, such as inheritance taxes.
To add more legal complexity to an already tangled system, the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) has recognized, in a recent ruling, that the model applied is discriminatory for non-residents in Spain, who From now on they will also be able to benefit from regional benefits. The amendment to adapt the ruling to the CJEU decision is still pending approval, but approval could arrive before the end of the year.
The consequences go far beyond choosing which region to live in, but can have a direct impact on the investment that comes from abroad. «As is now the case with residents in Spain, who change their domicile to autonomous communities in which their successors can totally or partially avoid the tax, non-residents, from now on, will take into account in which region they will open their businesses. bank accounts, they will invest their financial assets or buy real estate," explains Juan Fernández, partner at Rey Quiroga Fiscalistas and official on leave from the Tax Agency.
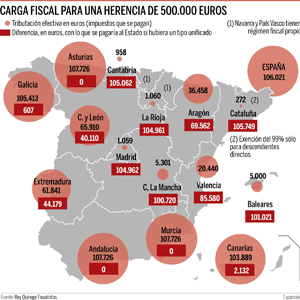
DifferencesThe differences could not be more disparate. According to calculations made by this office, Catalonia, Madrid and Cantabria are the autonomous communities where the least taxes are paid when inheriting, while Andalusia, Murcia and Asturias are closest to state regulations and, therefore, are the most expensive. . For example, for an inheritance valued at 500,000 euros, an Asturian will have to pay the Administration more than 100,000 euros, that is, around 21% of what they will receive. However, for the same amount, the effective taxation of a Catalan is 272.5 euros, that is, 0.05%, and that of a Cantabrian, 959 euros (0.19%).
In the case of Spanish citizens living abroad, the state rate previously applied, but when the reform comes into force, they will be able to benefit from the most advantageous situation. In your case, when your address cannot be linked to a specific CCAA, the region where the majority of the value of the assets is located will be taken into account, as explained by the partner of Rey Quiroga Fiscalistas.
Furthermore, this expert points out that these problems can also lead to an increase in "tax litigation", since the rules are not always clear. Furthermore, the CJEU ruling opens the way to a new wave of claims from those who have been affected by the regulations in force until now.
Fernando Sierra, director of the tax area at Novit Legal, emphasizes that in cases in which it is not possible to request the return of undue income because more than four years have passed since the income was made, "taxpayers may demand financial liability from the State; To start this procedure they have one year since the CJEU ruling was published on September 3 and could ask to be compensated for infringement of the community order regarding inheritance and gift tax.
The tax reform adapts the ruling of the Court of Justice of the EU - The Government will adapt Spanish legislation in the tax reform to the ruling of the Court of Justice of the European Union of last September 3, which considered the Spanish regulations on Inheritance Tax contrary to community law because it restricts the free movement of capital. Specifically, because it discriminates against non-residents in Spain and Spaniards who transmit or receive assets abroad. This was established by an amendment by the Popular Group in Congress.
– Regarding Inheritances, Spanish law establishes that those inheritances or donations in which one of the parties (the deceased, the donor or the beneficiary) is a non-resident cannot enjoy the tax reductions applied by each community. The same is true when it comes to assets abroad.
– The state rate is applied to these taxpayers, which entails a tax of between 7.65% and 34% and, in some cases, higher (see attached table). Another PP amendment in the Senate corrects the situation for heirs of non-resident parents without property in Spain, since Congress maintained the obligation of these heirs to pay taxes at the state rate and not at that of their autonomous community of residence. Now, these taxpayers, if the parent resides in the EU, will apply the rate of their autonomous community.
– This change brings to the table the conflict of differences created by the varied taxation of this tax in each region. The Constitutional Court is studying a question of unconstitutionality regarding this matter that was raised by the Supreme Court in 2013.
Fountain: www.expansion.com



